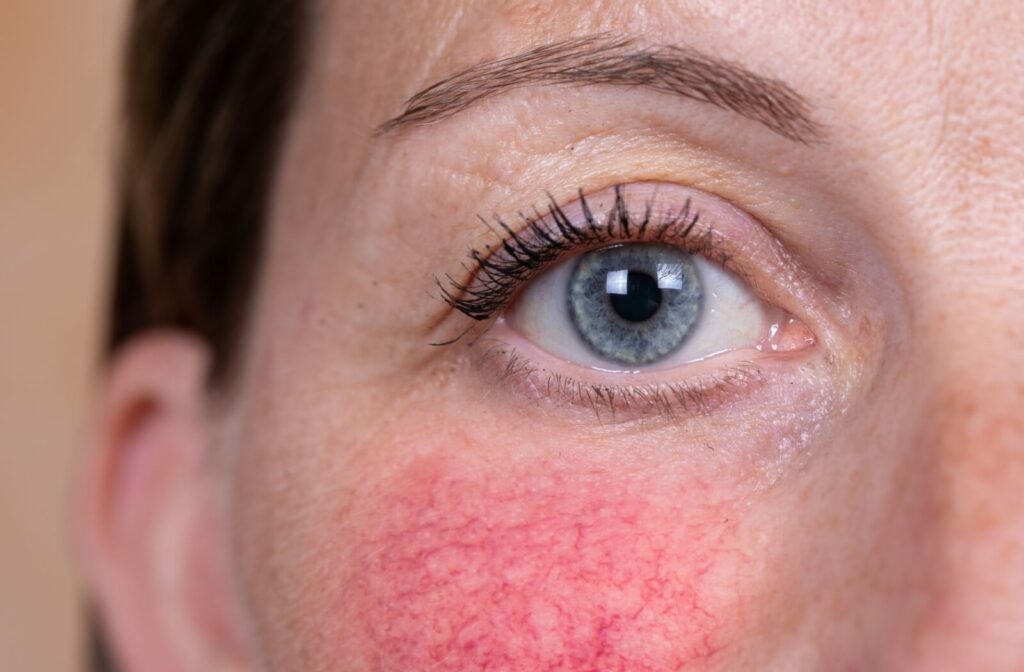
Rosacea is a chronic skin condition that sometimes affects your eyes. Experts aren’t sure what exactly causes rosacea, but it could be a symptom of another disease. A flare-up can be triggered by certain foods, stress, and other elements in the environment. Whether rosacea is an autoimmune disorder is still debated among researchers.
Rosacea that affects your eyes is called ocular rosacea, and dry eyes can be a symptom. If you’re experiencing symptoms of ocular rosacea or dry eye, an optometrist can help. Treatments can range from lifestyle changes and over-the-counter eye drops to modern technologies like intense pulsed light (IPL) therapy.
What Is Rosacea?
Rosacea is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that causes areas of redness on the nose and cheeks. It can also affect the eyes. This condition is more common among middle-aged and older adults, women, and people with lighter skin tones. However, it tends to be more severe when it appears in men. And it’s possible that rosacea is underdiagnosed in people with darker skin because the rash is harder to see.
Signs and symptoms of rosacea include:
- Flushing and blushing
- Pimples and other bumps that look like acne
- Thicker skin, especially in the nose area
- Blood vessels that are visible beneath the skin
- Itchy and burning sensations
- Skin that looks dry or appears rough
- Symptoms affecting the eyes, such as dry eyes, styes, and swollen eyelids
- Plaques, rashes, and swelling
Rosacea can present in slightly different ways among different people. Some people experience redness on their face; others have redness elsewhere on their body. Some people experience a certain progression of symptoms. Many people report cycles of flare-up and remission.
Is Rosacea an Autoimmune Disease?
Whether rosacea is an autoimmune disease remains debatable among experts, though it appears linked to the immune system. For example, one type of rosacea involves the body overcompensating in its immune response to a type of bacteria.
Rosacea may also be a symptom of an underlying health condition, an overgrowth of Demodex mites on the skin, an H. pylori infection, or a defect in the way the cathelicidin protein works. Environmental and genetic factors are also thought to contribute to rosacea.
Rosacea & Your Eyes
When rosacea affects your eyes, it’s called ocular rosacea. Some people have rosacea without ocular rosacea; others have ocular rosacea but no symptoms on other parts of their body. Symptoms of ocular rosacea include:
- Red eyes
- Watery eyes or discharge
- Burning sensations or discomfort
- Feeling that there’s a foreign object lodged in your eye
- Red or inflamed eyelids
- Clogged oil glands around the eyelids
- Sensitivity to light
Ocular rosacea is also linked to eye conditions like conjunctivitis (pink eye), chalazions, styes, and dry eye.
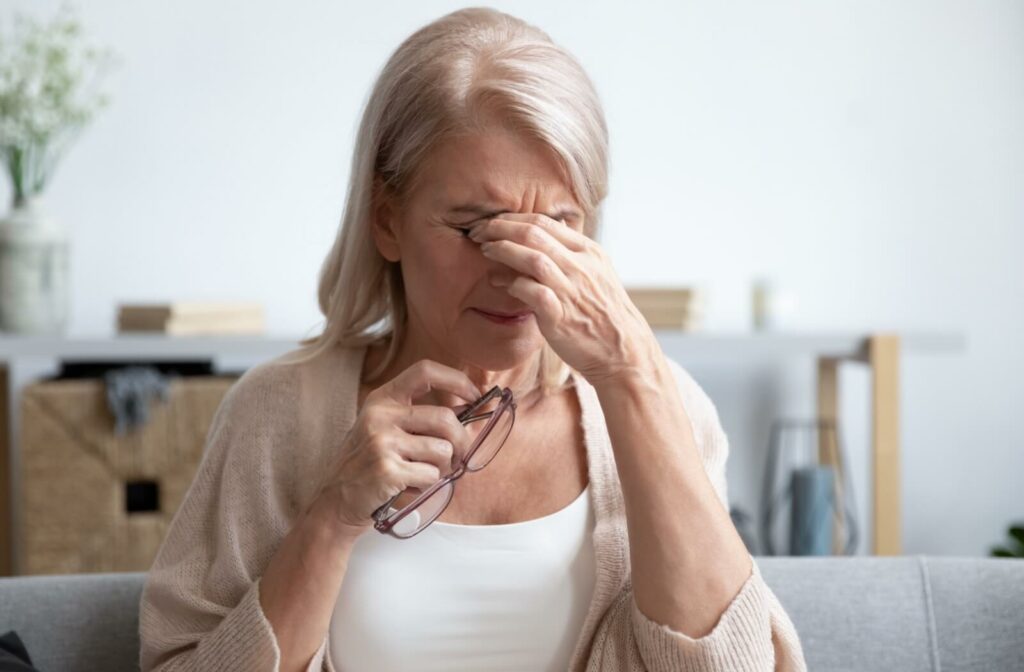
Causes of Dry Eye
If you’re experiencing dry eye, it’s important to investigate the underlying cause of your symptoms. Rosacea is linked to dry eye, but there are many other possible causes, such as:
- Environmental triggers, such as smoky places or areas with low humidity
- Lifestyle factors, such as prolonged screen time
- An underlying health issue, such as diabetes, thyroid problems, and autoimmune disorders
- Side effects of an unrelated medication

Treatments for Dry Eye & Ocular Rosacea
Schedule an eye exam with an optometrist if you have symptoms of dry eye or ocular rosacea. Your optometrist should take into account your personal and family medical history when diagnosing the cause of your symptoms.
Managing Dry Eye
Treatments for dry eye include:
- Lifestyle changes: Limit screen time, stay hydrated, and get 7 to 8 hours of sleep a night.
- Eye drops: Some require a prescription, but artificial tears are often available over-the-counter. However, it’s a good idea to get a professional recommendation from your optometrist, especially if you have other health conditions or take other medications.
- Light-based treatments: Intense pulsed light (IPL) therapy can help unblock oil glands that may be at the root of your dry eye symptoms.
Managing Ocular Rosacea
While there is no cure for ocular rosacea, there are ways to manage your symptoms. These include:
- Knowing and avoiding your triggers: Common triggers include UV light, alcohol, spicy foods, stress, intense heat or cold, physical exercise, and stress.
- Eye treatments: Eye drops, artificial tears, and certain eyelid cleansers can help. Ask your optometrist for suggestions on what products to use.
- Warm compresses: Try applying a warm compress to your closed eyes during a bath or immediately after.
- Sunscreen: Use a sunscreen with SPF 30 or higher. Wearing sunscreen is a healthy daily habit, even for people with healthy skin, as it protects against skin cancer.
- Antibiotics: Sometimes, doxycycline can be an appropriate treatment when prescribed.
Eye & Skin Care in Long Beach
Ocular rosacea and dry eye can have a significant impact on your productivity and everyday life, but options are available to relieve symptoms. At Sea View Optometry, we offer intense pulsed light (IPL) treatment. IPL can treat dry eye by unblocking the glands in your eyelids that secrete oil. We also offer skin care treatments.
Sea View Optometry has been serving the Long Beach community since 1996. We strive to provide a healthcare experience that’s not only comprehensive but also empathetic and inclusive of folks from all walks of life. Learn more about us or book an appointment today!